Material of measurement
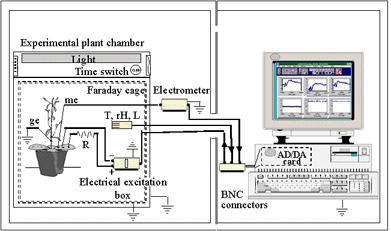
Extracellular plant biopotential measurement (EPBM) installation for electrophysiological computer-assisted measurements of potential A. thaliana plants. The whole installation is compartimented between two rooms. The first is thermo-and hygro-regulated and contains the experimental plant chamber with A. thaliana, the light, the sensors, and the Faraday cage. The light is provided with fluorescent tubes and controlled by a timer. In the second independent room the computer is installed to allow the real-time monitoring and control of the experiment with a specific software. The A/D part card of the computer receives the signal from the measuring electrode (me, +) positioned on a leaf (or another part of the plant) with respect to a symmetrical reference electrode (re, -) positioned on the soil, through the electrometer. A ground copper electrode (ge) is also inserted in the soil. The electrodes (me, re) consist of a small tube ended by a cotton and filled with an electrophysiological solution containing 1 mM KCl; 0.1 mM CaCl2; 50 mM sorbitol, in contact with a chlorinated silver wire (Ag/AgCl, 0.125mm). The electrometer is a home-made circuit based on the INA 116 (1015
Bioelectrogenesis emulation induced by the light or the darkness:
Have more details
The Plant Action Potentials (APs) - I -:
- The Liverwort Conocephalum conicum can easily trigger APs by mechanical or electric stimulations.

Measuring device for studing electric potentials in C conicum. A thallus is washed then put in a box of Petri containing a filter soaked with electrophysiological solution. The bioelectric response after 3 seconds of electrical stimulation to 1.8 Volts (Stim. -, Stim +) is a AP which is propagated from the electrode C.1 to C.2 to C.3 (dashed arrows).
The Plant Action Potentials (APs) - II -:
- Arabidopsis thaliana which is the genetic model of higher plants, does not have an evidence of triggering APs by electric stimulations. However, our group of research has developed a method of stimulation allowing to start a series of APs (cf. favre et al., 2001 -> see publications):
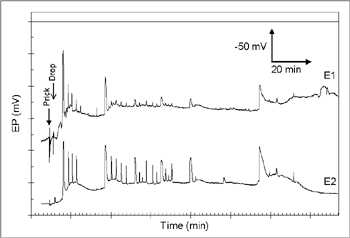
Series of APs recorded on the petiole of A. thaliana. APs are induced after stimulation of the extremity of the leaf (Prick and Drop).